PARLIAMENTARY COMMITTEES
A parliamentary committees is a group of MPs appointed by one or both Houses
of Parliament to undertake certain specified tasks.
Conditions
- Is appointed or elected by the House or
nominated by the Speaker/Chairman - Works under the direction of the
Speaker/Chairman - Presents its report to the House or to the
Speaker/Chairman - Has a secretariat provided by the Lok
Sabha/Rajya Sabha
Limitations
- Financial committees conduct a post-mortem
examination of accounts - Cannot intervene in the matters of day-to-day
administration. - Recommendations are advisory and not binding
on the ministries - Not executive bodies and hence, cannot issue
an order
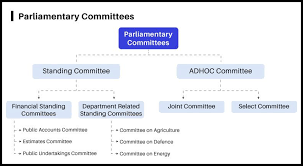
Types
Ad hoc
- Temporary
- For specific purpose
- Ceases to exist once the
task is over
Standing
- Permanent
- Formed every year
- 6 categories
Select
- Members of one House
only - E.g., Estimates Committee
Joint
- Consists of members of
both the Houses - E.g., PAC, DRSCs
STANDING COMMITTEES
Financial Committees
Departmentally-related Standing Committees
Committees to Inquire
Committees to Scrutinise and Control
Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business
of the House
House-Keeping Committees or Service
Committees
FINANCIAL COMMITTEES
- Public Accounts Committee
- Estimates Committee
- Committee on Public Undertakings
Contribution
- Examination of Public Expenditure
- Ensuring Accountability
- Financial Transparency
- Non-partisan Functioning
- Highlighting Irregularities
- Recommendations for Improvement
- Enhancing Public Confidence
- Follow-up on Audit Reports
- Promoting Efficiency and Economy
- Legislative Oversight
Limitations
- Limited Jurisdiction
- Non-Consideration of All CAG Reports
- Political Bias
- Lack of Expertise
- Limited Powers
- Public Perception and Media Coverage
- Executive Resistance
- Impact of Parliamentary Disruptions
- Need for Modernization and Capacity Building
Estimates Committee
- Set up first in 1921;
- Members – 30 (LS – 30, RS – 0)
- Functions
vExamination of Budget Estimates: This committee scrutinizes the
budget estimates presented by the government.
vSuggesting Economies in Operations: It suggests alternative policies
to bring about efficiency and economy in administration.
vContinuous Review of Government Work: The Estimates Committee
keeps an ongoing check on government spending and policies.
vAssisting in Policy Formulation: It assists Parliament in its detailed
study of the budget and in understanding the ways in which money is
spent
Issues
- Limited Expertise of Members
- Scope of Work
- Non-Binding Recommendations
- Volume of Work
- Partisan Influences
- Lack of Public Awareness and Transparency
- Time Constraints
- Implementation of Recommendations
- Inadequate Research Support
- Effectiveness in Question
Public Accounts Committee (PAC)
- Set up first in 1921
- Members – 22 (LS – 15, RS – 7)
- Functions
qExamine the appropriation accounts and the finance accounts
of the Union government
qExamine audit reports of CAG
Contribution
- Examination of Public Expenditure
- Ensuring Accountability
- Financial Transparency
- Non-partisan Functioning
- Highlighting Irregularities
- Recommendations for Improvement
- Enhancing Public Confidence
- Follow-up on Audit Reports
- Promoting Efficiency and Economy
- Legislative Oversight
Limitations
- Limited Jurisdiction
- Non-Consideration of All CAG Reports
- Political Bias
- Lack of Expertise
- Limited Powers
- Public Perception and Media Coverage
- Executive Resistance
- Impact of Parliamentary Disruptions
- Need for Modernization and Capacity Building
Estimates Committee
- Set up first in 1921;
- Members – 30 (LS – 30, RS – 0)
- Functions
vExamination of Budget Estimates: This committee scrutinizes
the budget estimates presented by the government.
vSuggesting Economies in Operations: It suggests alternative
policies to bring about efficiency and economy in
administration.
vContinuous Review of Government Work: The Estimates
Committee keeps an ongoing check on government spending
and policies.
vAssisting in Policy Formulation: It assists Parliament in its
detailed study of the budget and in understanding the ways in
which money is spent
Issues
- Limited Expertise of Members
- Scope of Work
- Non-Binding Recommendations
- Volume of Work
- Partisan Influences
- Lack of Public Awareness and Transparency
- Time Constraints
- Implementation of Recommendations
- Inadequate Research Support
- Effectiveness in Question
Departmentally-related Standing Committees
- Under RS (8): Commerce, Home Affairs, HRD, Industry,
Science & Tech., Transport, Health, Law - Under LS (16): Agriculture, IT, Defence, Energy, External
Affairs, Finance, Food, Labour, Petroleum, Railways,
Urban Development, Water, Chemicals, Rural
Development, Social Justice, Coal
Functions
- Scrutinize budget
- Examine bills referred to it by the Parliament
- Consider long-term basic policy documents
- Consider annual reports of Ministries/Departments
Problems
- Membership – political consideration
- Attendance – poor
- Meeting – irregular
- Government usually in a hurry to get the bills
passed - Recommendations not usually accepted by the
Ministries.
Recommendations
- Membership should be based on expertise in domain.
- Sending Bills to DRSCs should be automatic.
- Fixed time-line for DRSCs to submit reports.
- Suggestions of DRSCs should be ideally binding.
- Inviting outside experts (from private sector).
Committee on Ethics
- Established:
-Lok Sabha – 2015
-Rajya Sabha – 1997 - Functions:
-Lay down code of conduct for members
-Supervise the ethical and moral conduct
of members - Complaint Mechanism:
-Any citizen can complain against an MP
-Presiding Officer forwards complain to
Committee.
-Voting takes place on Committee’s report
in the House
| Name of the Committee | LS MPs | RS MPs | Chairman | CAN MINISTER BE A MEMBER |
| Public Accounts (J) | 15 | 7 | Opposition | NO |
| Estimates | 30 | – | Ruling Party | NO |
| Public Undertakings (J) | 22 | 7 | By P/O | NO |
| DRSC (J) | 21 | 10 | By P/O | NO |
| Petitions (S) | 15 | 10 | By P/O | NO |
| Govt. Assurances (S) | 15 | 10 | By P/O | NO |
| Business Advisory Committee (S) | 15 | 11 | PRESIDING OFFICER | – |
| Papers Laid on the Table (S) | 15 | 10 | By P/O | – |
| Subordinate Legislation (S) | 15 | 15 | By P/O | NO(LS) |
| Rules (S) | 15 | 16 | PRESIDING OFFICER | – |
| Welfare of SC/ST (J) | 20 | 10 | By P/O | NO |
| Welfare of Women (J) | 20 | 10 | By P/O | NO |
| Privileges (S) | 15 | 10 | By P/O | – |
| Ethics (S) | 15 | 10 | By P/O | – |
Committee on Ethics
Established:
-Lok Sabha – 2015
-Rajya Sabha – 1997
Functions:
-Lay down code of conduct for members
-Supervise the ethical and moral conduct
of members
Complaint Mechanism:
-Any citizen can complain against an MP
-Presiding Officer forwards complain to
Committee.
-Voting takes place on Committee’s report
in the House

