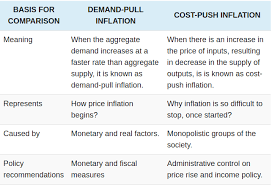
Inflation
- Inflation: “Inflation is the sustained rise in the average prices
of a basket of goods and services”.
Types- According to the magnitude of inflation.
- According to the sources of inflation.
Types of inflation-based on rate
- Moderate (Low and stable – single digit)
- Galloping (High and unstable – double or triple digit)
- Hyperinflation (Extreme and uncontrollable – very large
numbers)
Two measures of Inflation
WPI (Wholesale Price Index)
- Captures the price changes in the wholesale market (B2B).
- Excludes the services sector.
- Base year = 2011-12
CPI (Consumer Price Index)
- Captures the price changes in the retail market (B2C).
- Includes both goods and services.
- Base year = 2012
WPI
- Base year updated from 2004-05 to 2011-12.
- The number of items has been expanded from 676 to 697.
- A total of 199 new items have been included and 146 old items have been excluded.
- Based on the suggestions from Saumitra Chaudhuri working committee.
- Provided by Economic Advisor (Commerce Ministry).
- Released once a month.
| base year (2011-12) | ||
|---|---|---|
| number of items | weight | |
| primary articles | 117 | 22.62 |
| fuel and power | 16 | 13.15 |
| manufactured items | 564 | 64.23 |
| total | 667 | 100 |
WPI – Ramesh Chand Committee
- Include both goods and services in the calculation.
- Increase the number of items in the basket from
697 to 1196. - Update the base year to 2017-18.
- Suggest adding more products to the list
- Herbal plants (aloe vera, menthol, fennel seed etc).
- Green tea, sanitizers, mushrooms, brown rice etc.
CPI
Previously three different types – IW, UNME and AL.
- Changed to CPI (Combined), CPI (Urban) and CPI (Rural)
- Number of items
- Rural = 448
- Urban = 460
- Combined = 299
- Base year = 2012
- Calculated by NSO
| Industrial Workers(IW) | Urban Non-Manual Employees(UNME) | Agricultural Labours (AL) | |
| base year | 2016 | 1984-85 | 1986-87 |
| number of articles | 463 | 180 | 60 |
| services included | yes | yes | no |
| published by | ministry of labour | MoSPI (Ministry of statistics and programme implementation) | ministry of labour |
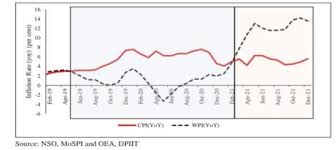
CPI & WPI – Divergence
Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT)
- The government has delegated the responsibility of managing inflation to RBI.
- MPFA was agreed upon by GoI and RBI.
- It was signed in 2015 and implemented from 2016.
- The government has modified the RBI Act for this purpose.
- Under this framework, the central government has set the inflation target in
consultation with RBI. - According to this, RBI has to keep inflation at 4% (with a margin of 2% on either
side). - If inflation deviates from the 4% target by more than 2% for three consecutive
quarters, then RBI has to justify to the government the reasons and the measures
to restore inflation within the range. - Every 6 months, it has to publish a report indicating-the current level and the
expected trend of inflation. - The experience for last five years has shown that
- The inflation rate has stayed within the target range (2% to 6%) for most of
the time despite the uncertainties and shocks in the economy - One of the factors driving up the inflation rate in recent months has been
supply-side constraints such as rising commodity prices, which are outside
the RBI’s influence - The average inflation rate for five years (until 2021) has been around
3.47%, compared to the average of 5.7% for five years before the inflation
targeting regime - The monetary policy making process has become more transparent
Inflation Targeting – headline or Core?
Headline Inflation
- The common people are mostly affected by the rising prices of food and fuel.
- Inflation has been brought under control since the inflation target was introduced in
2016, after being in double digits for a long time. - This is not the right time to make a policy change that would allow RBI to relax its focus
on price stability.
Core Inflation
- Core inflation is a more reliable measure of inflation than headline inflation.
- Headline inflation includes the commodities whose prices fluctuate a lot.
- Price volatility may hamper the policy making process.
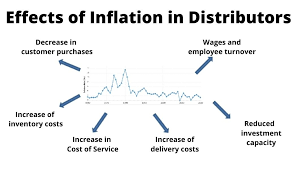
Effects of inflation
- Erodes purchasing power – the same amount of money can buy fewer
goods and services. - Lowers real rate of returns
- Returns after accounting for inflation.
- The higher the inflation, the lower the real rate of returns.
- Exports – country with higher inflation, exports become less competitive.
- Impacts investment climate.
How to control inflation?
- Reduce the money supply – RBI through the monetary policy.
- Government reduces the expenditure.
- Government increases the income tax rate.
- Households start saving more.
- Increase the production.
Other concepts
- Deflation: A decline in the average prices of goods and services.
- Disinflation: A reduction in the inflation rate or a slower increase in prices.
- Core inflation: The inflation rate that excludes the volatile items (such as food
and energy) that may distort the overall trend. - Headline inflation: The inflation rate that includes all the items in the basket of
goods and services. - Inflation Tax
- It is the loss of value of money as the prices of goods and services increase.
Stagflation - A condition where the economy faces high inflation and high unemployment at
the same time. - It is a mix of inflation and stagnation.
Base effect - The influence of the price level of the base period on the calculation of the
inflation rate in the current period. - Skewflation :
- A condition where some goods and services experience inflation while
others experience no inflation or deflation. - It was observed in India in the previous decade.
Reflation : - A policy of the government to boost the output or the growth of the
economy to overcome a slump or a contraction. - Imported inflation
A rise in the general price level due to an increase in the cost of imported
goods or services. - Wage price spiral
A feedback loop in which higher inflation leads to higher wages, which in
turn fuels more inflation.
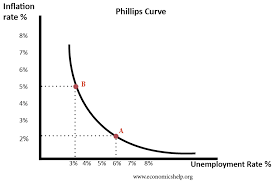
Phillips Curve
- A curve that shows the negative relationship between the inflation rate
and the unemployment rate.
Nominal (Current) and Real (Constant)
nominal= based on current market prices
real= based on prices in base year
GDP Deflator
- A measure of inflation that compares the current and base year prices of
all goods and services produced in an economy. - Indicates how much the GDP has grown due to higher prices rather than
higher output. - Includes a wider range of goods and services than other price indices.
GDP= Nominal/Real GDP
Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary
in its effects? [2021]
a) Repayment of public debt
b) Borrowing from the public to finance a budget deficit
c) Borrowing from the banks to finance a budget deficit
d) Creation of new money to finance a budget deficit
option d

