Federalism is a System of government that separates the power between
central government and regional government of the country.
Indian Federalism
Federation sui generis
Federal Features
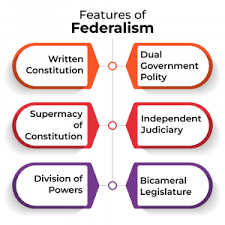
- Dual polity
- Division of Powers
- Written Constitution
- Supremacy of the Constitution
- Independent judiciary
- Bicameral legislation
- Rigidity of federal provisions in Constitution
Unitary Features
- Division of power is not equal (Subjects, Residuary powers, Fiscal
powers) - Central control over states (State List, Appointment of Governor,
Fiscal powers) - Single Constitution
- The constitution is more flexible than rigid
- Single Citizenship
- Common machinery (elections, audit etc.)
- Parliament does not represent the states equally
- Unified judiciary
- Emergency provisions
- All India Services
- Destructible states
- Weak Rajya Sabha
Cooperative Federalism
- Concurrent List
- All India Services
- DPSPs
- Immunity of Instrumentality
- No division of public services
- Duty of centre to protect states (Art 355)
Asymmetric Federalism
- Representation in RS
- Special Category States
- Schedule V & VI areas in certain states
- Uneven fiscal devolution amongst states
- Creation and administration of UTs
Competitive Federalism
- NITI Aayog
- Freedom to plan its expenditure based on its priorities.
- Various Rankings released by Ministries/organisations.
what is fedaralism
Federalism is a System of government that separates the power between
central government and regional government of the country.
