Types Of Goods
In it we know about types of goods
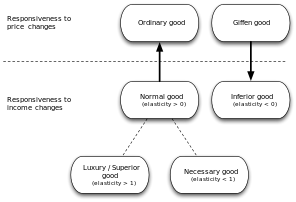
Based on Income
NORMAL
- Demand increases as income increases (positive relationship).
- Income elasticity of demand is positive.
- Examples: TV, Refrigerator, Cars, etc.
INFERIOR- Demand decreases as income increases (negative relationship).
- Income elasticity of demand is negative.
- Examples: Cereals, Public transportation, etc.
Types of Goods
Based on Prices
- GIFFEN
⚬ Demand increases as price increases.
⚬ This is due to the substitution effect.
⚬ These are usually basic goods consumed by the low-income group. - VEBLEN
⚬ Demand increases as price increases.
⚬ This is due to the prestige effect.
⚬ These are usually expensive goods that signify wealth and status.
Types of Goods
Based on Utility to Society
Merit
- Goods that benefit society when consumed.
- The government usually provides or subsidises them to
encourage consumption. - Examples: basic needs, health care, education, etc.
Demerit- Goods that harm the society when consumed.
- Negative spillover effect or externality.
- Examples: alcohol, tobacco, etc.
Types of Goods
Based on who is the producer
- Public (are non-rival and non-excludable)
⚬ Non-rivalry (using this good does not affect its availability for others).
⚬ Non-excludable (everyone can use this good without paying for it).
⚬ Examples: defence, streetlight, law and order (police). - Private (are excludable and rival)
⚬ Rival (using this good reduces its availability for others).
⚬ Excludable (only those who pay for this good can use it).
⚬ Examples: clothes, food, cars.
Types of Goods
Excludable Non–Excludable
| private goods Rival eg..cars | common goods Rival eg..public library |
| club goods Non Rival eg..electricity | public goods Non Rival eg…defence |
Types of Goods
Based on presence in the economic flow
- Intermediate
⚬ Are inputs for producing other goods or services.
⚬ Are part of the production process or supply chain.
⚬ Examples: steel, aluminium, coal, etc. - Final
⚬ Are ready for consumption or use by the end users.
⚬ Do not undergo any further processing or value addition.
⚬ Examples: car, cell phone, etc.
Types of Goods
Substitute goods
- Goods that can replace each other to satisfy the same need.
- Can be switched.
- Demand changes with the price of the good or its substitute.
- Examples: tea and coffee; cold drinks, cars, mobiles, etc.
Complementary goods- Goods that are used together to satisfy a need.
- Cannot be separated.
- Demand changes with the price of the good or its complement.
- Examples: petrol/diesel and car; ink and printer, etc.
how many types of goods are there…
there are 14 types of goods…..
